Notes of Basic Concepts in GPU Computing
本文将以NVIDIA GPU为例,结合CUDA,记录下GPU中的基本概念。本文默认以Fermi architecture为例,同时内容会逐步完善!
Terms
- SP(Streaming Processor)
- SM(Streaming MultiProcessor)
- Warp(线程束)
CPU vs GPU
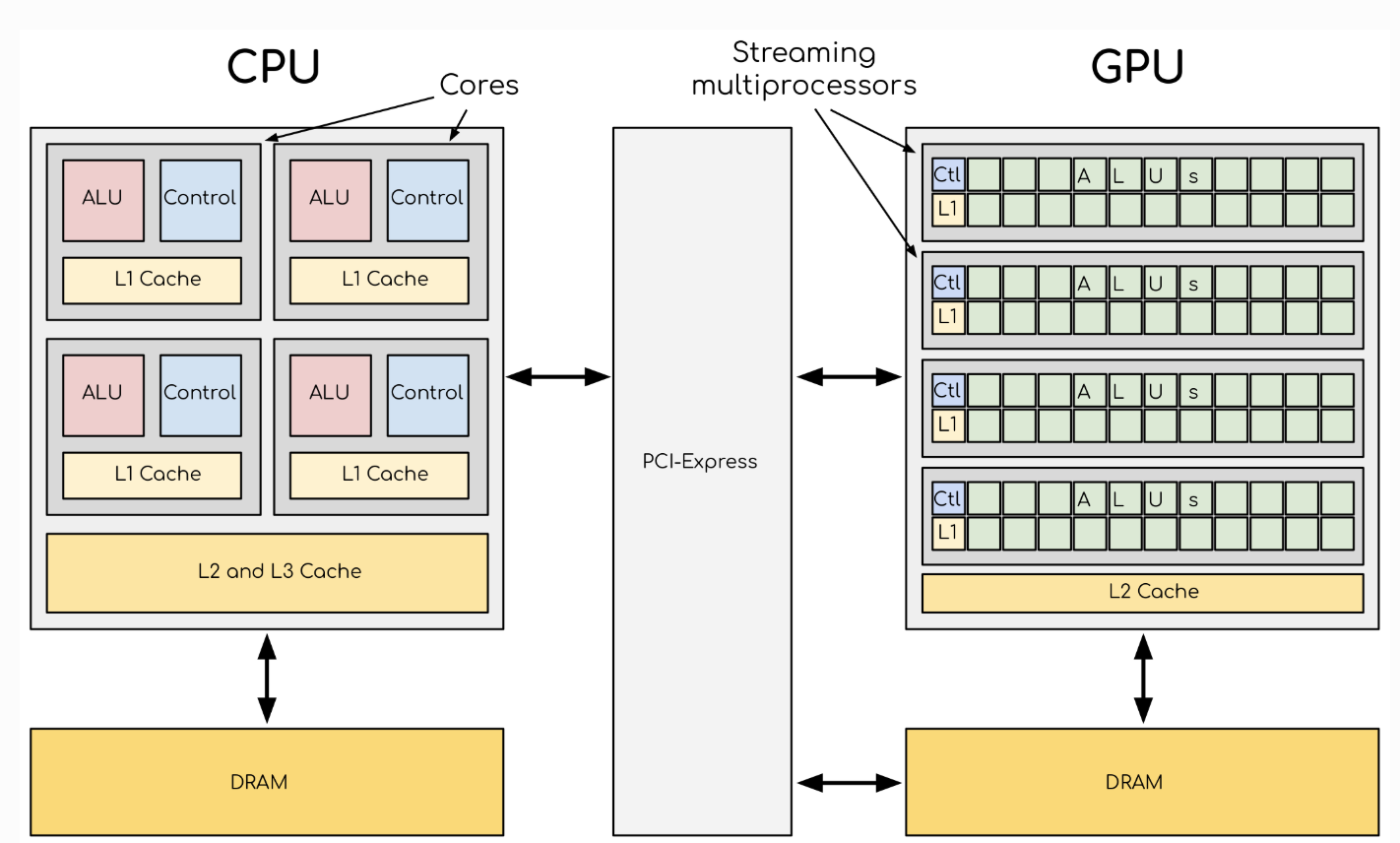
CPU has complex core structure and pack several cores on a single chip. GPU cores are very simple in comparison, they also share data and control between each other. This allows to pack more cores on a single chip, thus achieving very high compute density.
Components
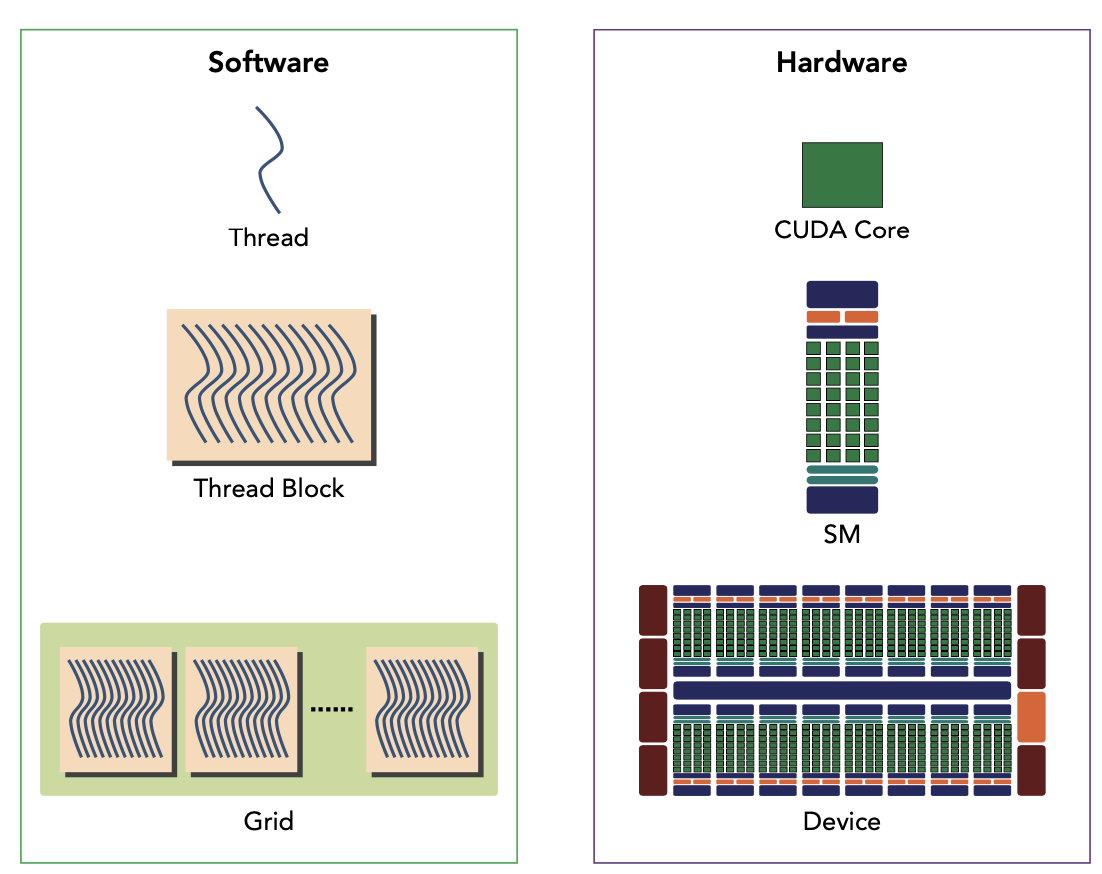
Hardware’s View
SP(Streaming Processor):是GPU最基本的处理单元,在fermi架构开始被叫做CUDA core。
SM(Streaming MultiProcessor): 一个SM由多个CUDA core组成,每个SM根据GPU架构不同有不同数量的CUDA core,Pascal架构中一个SM有128个CUDA core。
Software’s View
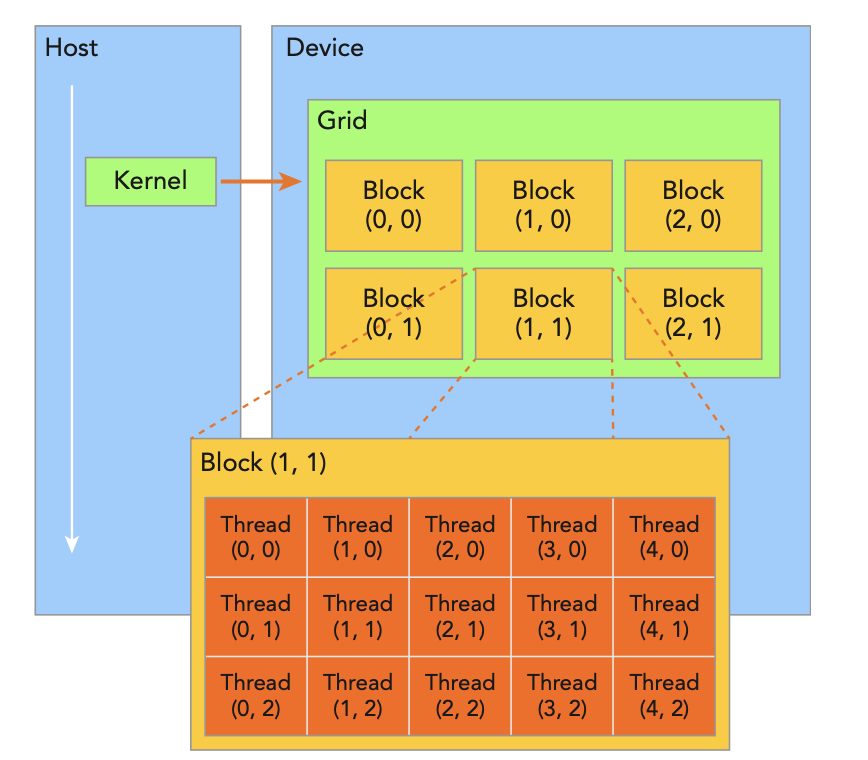
- thread: 一个CUDA并行程序会以许多个thread来执行
- block: 数个thread会组成一个block
- grid: 多个block则会再构成grid
GPU Architecture
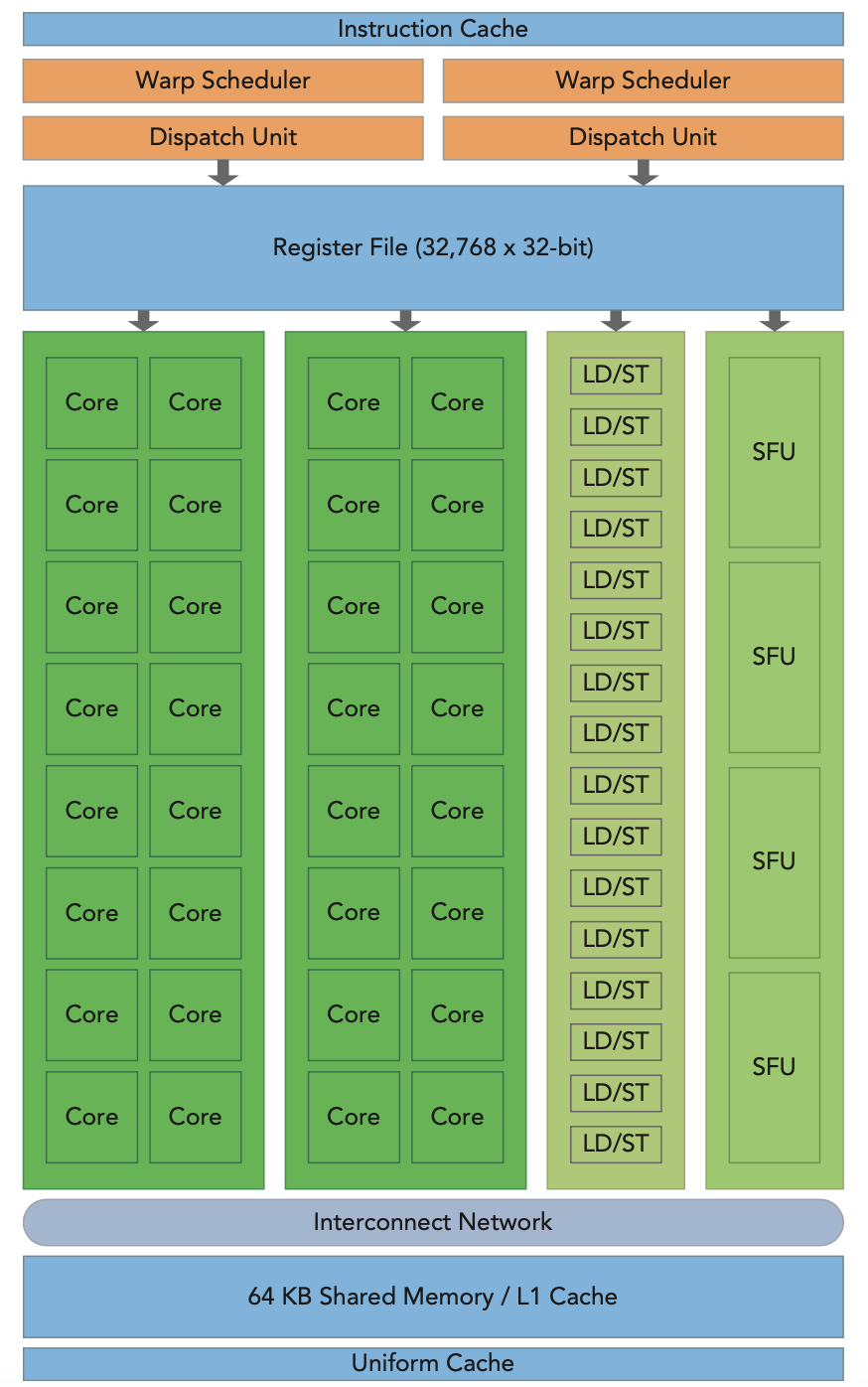
The following graph shows the Fermi architecture. This GPU has 16 streaming multiprocessor (SM), which contains 32 cuda cores each. Every cuda core is an execute unit for integer and float numbers.
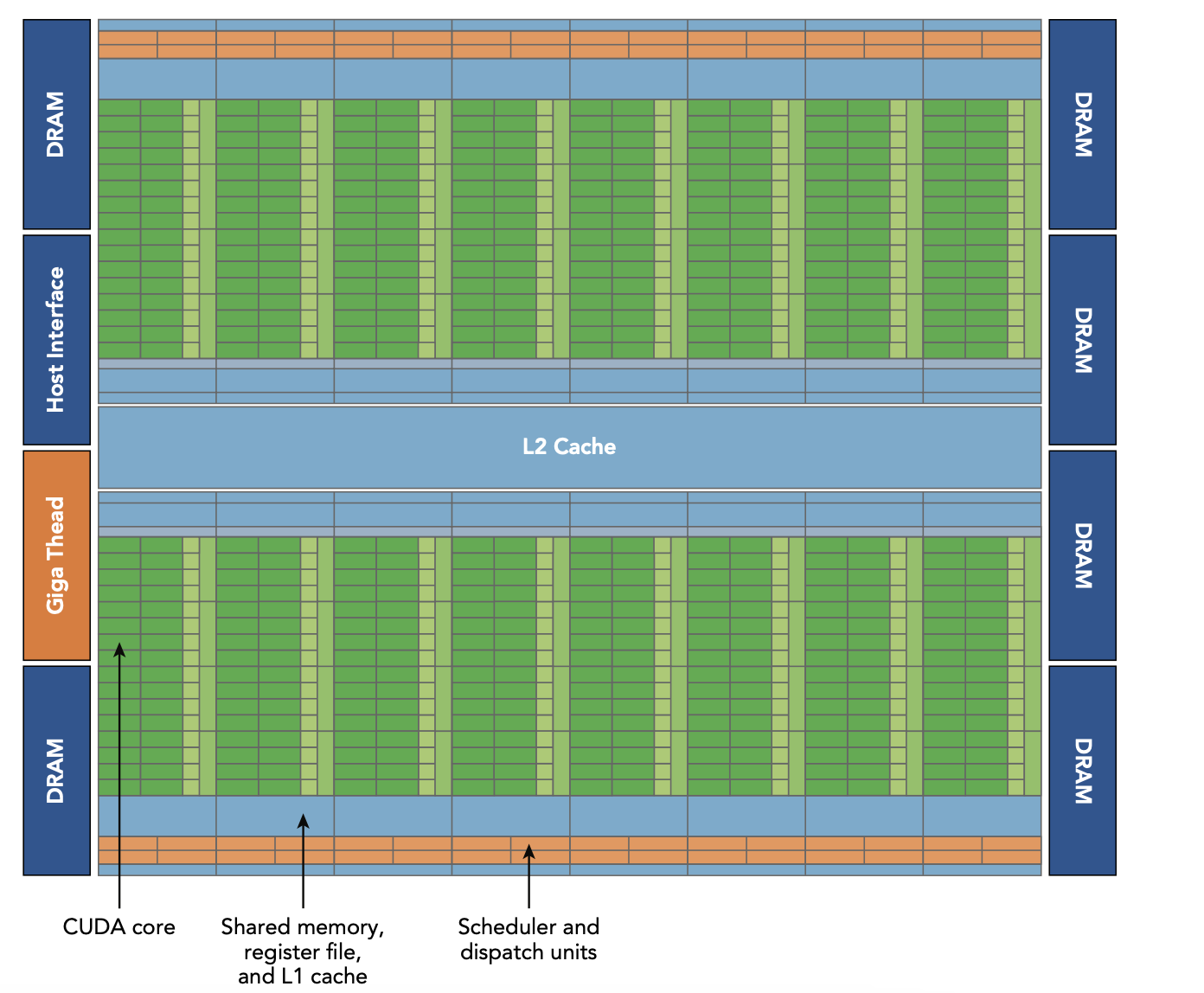
As shown in the following chart, every SM has 32 cuda cores, 2 Warp Scheduler and dispatch unit, a bunch of registers, 64 KB configurable shared memory and L1 cache. Cuda cores is the execute unit which has one float and one integer compute processor. The SM schedules threads in group of 32 threads called warps. The Warp Schedulers means two warps can be issued at the same time.
Warp
Each SM features two warp schedulers and two instruction dispatch units. When a thread block is assigned to an SM, all threads in a thread block are divided into warps. The two warp schedulers select two warps and issue one instruction from each warp to a group of 16 CUDA cores, 16 load/store units, or 4 special function units. (虽然硬件上1个warp只有16个CUDA cores,逻辑上1个warp有32个thread,可以通过硬件花费两个周期来处理完32个thread,也就是16个cuda cores执行了两个周期来运行这32个thread)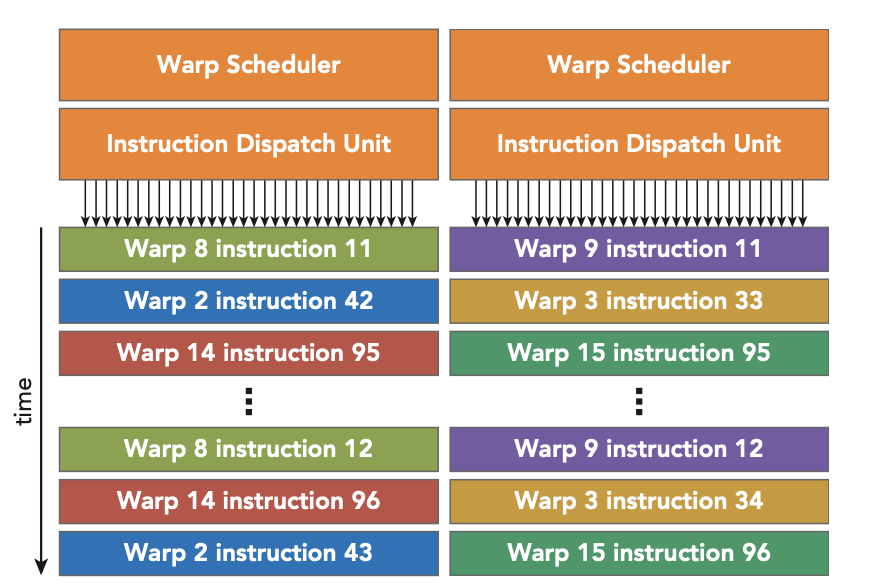
Warps are the basic unit of execution in an SM. When you launch a grid of thread blocks, the thread blocks in the grid are distributed among SMs. Once a thread block is scheduled to an SM, threads in the thread block are further partitioned into warps. A warp consists of 32 consecutive threads and all threads in a warp are executed in Single Instruction Multiple Thread (SIMT) fashion; that is, all threads execute the same instruction, and each thread carries out that operation on its own private data.
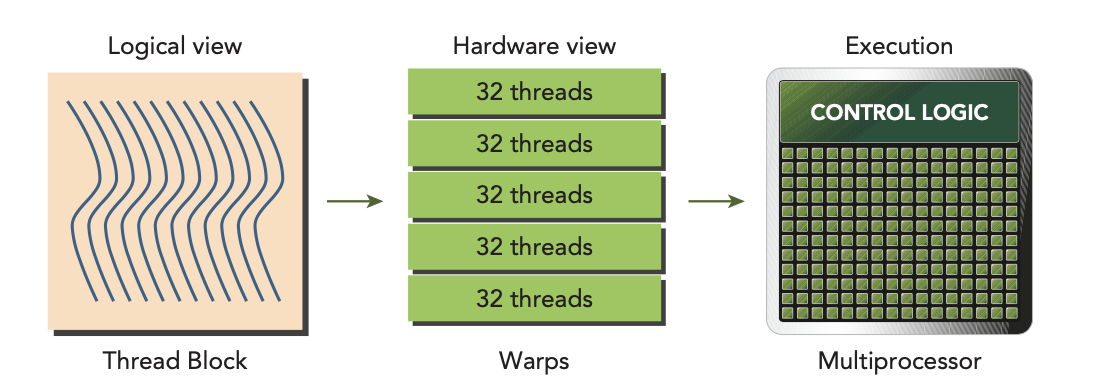
The number of warps for a thread block can be determined as follows: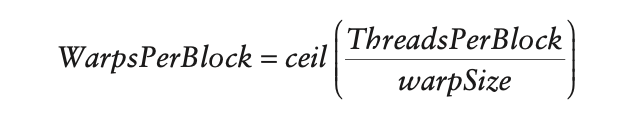
SM 是 Warp 的物理载体
SM 作为 GPU 的核心计算单元,负责承载并执行 Warp。每个 SM 可同时管理多个 Warp,通过硬件调度器动态分配资源。Warp 是 SM 的调度单位
Warp 由 32 个同步线程组成,是 SM 内指令发射的最小单元。SM 的 Warp 调度器 会从就绪的 Warp 中选择指令,分发至 CUDA Core、Tensor Core 等执行单元。资源竞争与负载平衡
SM 的寄存器、共享内存等资源限制了可驻留的 Warp 数量。若 Warp 因内存访问延迟阻塞(约 400-800 周期),调度器会立即切换至其他就绪 Warp,避免计算单元空闲。指令分发
- SM 的 Warp 调度器 从就绪的 Warp 中选择指令,分发至 Core 执行
- 例如:一个 Warp 的 32 个线程同时执行加法指令,调度器将其分配到 32 个 CUDA Core 并行处理
资源映射
- Hopper 架构:每个 SM 子分区含 32 个 FP32 Core,可直接匹配一个 Warp 的 32 线程,单周期完成指令
- 旧架构(如 Fermi):16 个 FP32 Core 需两周期处理一个 Warp
Memory Hierarchy
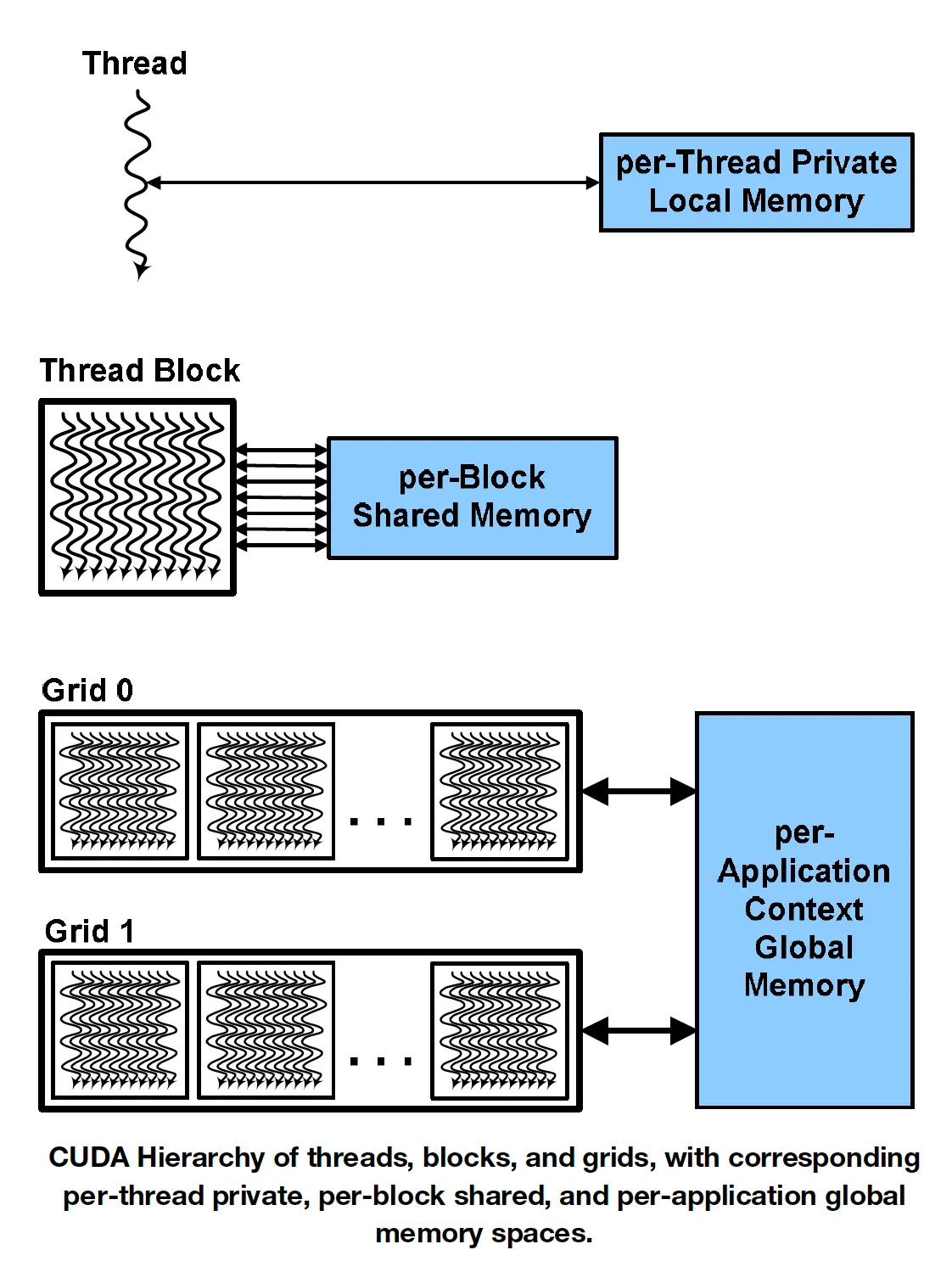
Shared memory is allocated per block. The shared memory per block is limited by the shared memory per SM.
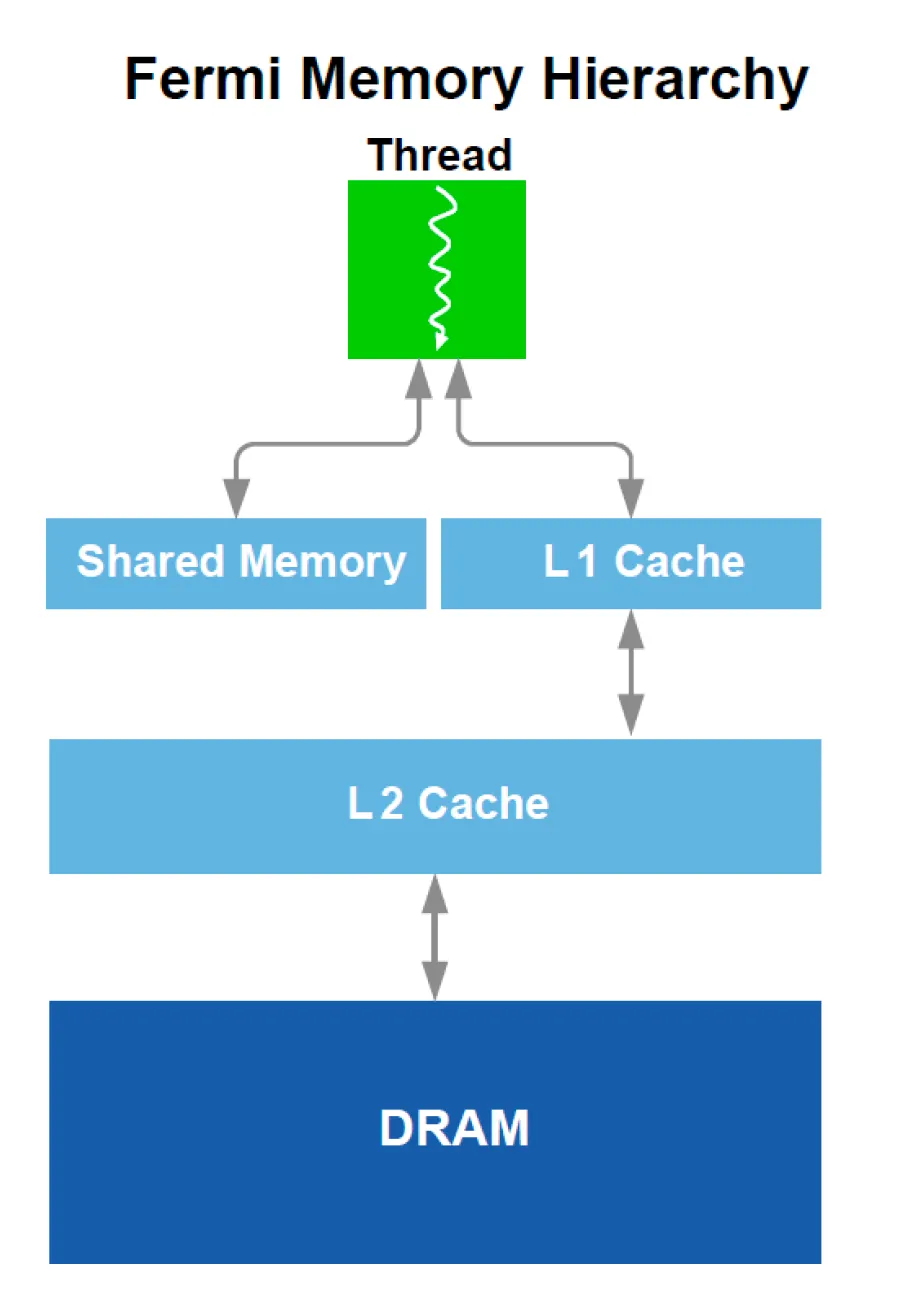
The fastest memory is registers just as in CPU. L1 cache and shared memory is second, which is also pretty limited in size. The SM above can have 48KB shared memory and 16KB L1 cache, or 16KB shared memory and 48KB L1 cache. L1 cache caches local and global memory, or only local memory varying among different GPU model. L2 cache caches local and global memory. Global memory acts like the ram in CPU computation, which is much slower than L1 and L2 cache.
参考资料: