Notes about jumbo frames and Path MTU Discovery
本文将mark下jumbo frames和Path MTU Discovery(PMTUD)的相关notes。
jumbo frames
巨型帧(Jumbo Frames)是指有效负载超过IEEE 802.3标准所限制的1500字节的以太网帧。目前阿里云支持8500字节的巨型帧,即允许您发送8500字节载荷的以太网帧。
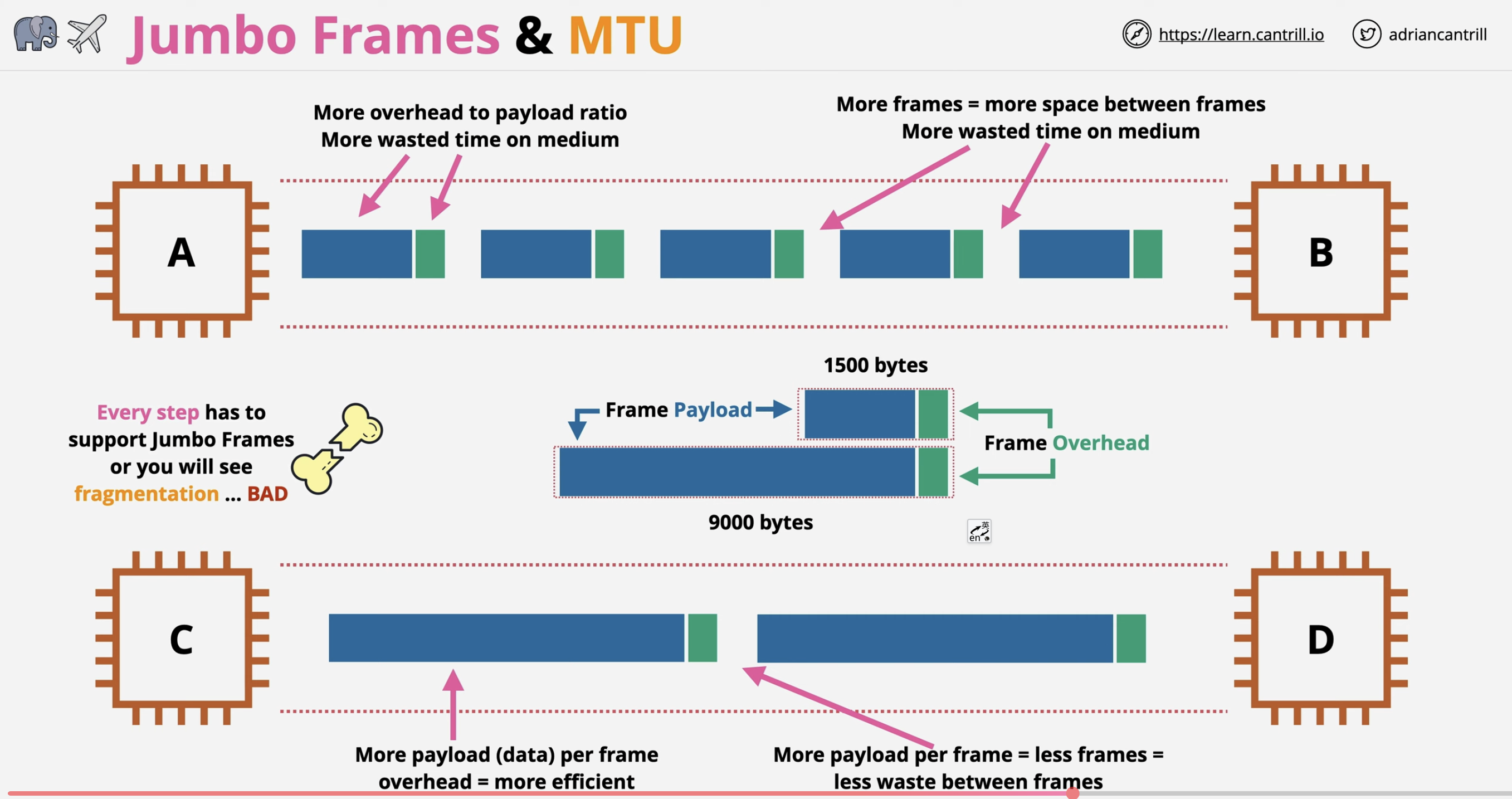
Supporting jumbo frames is crucial for enhancing bandwidth and transmission efficiency. It increases the effective payload per packet, reducing performance pressure on forwarding components.
巨型帧通过增加帧的大小,每个数据包可以携带更多数据,从而减少了所需传输的数据包数量,降低了处理器的负担并提高了整体数据传输速度。在需要高吞吐量和大带宽的网络环境中,特别是在数据中心、服务器场和高速网络互联等传输大量数据的场景中,使用巨型帧有助于减少网络传输耗时和提升网络效率,充分发挥网络性能。
PMTUD
Background
TCP分段了,IP层就一定不会分片了吗?
在发送端,TCP分段后,IP层就不会再分片了。但是整个传输链路中,可能还会有其他网络层设备,而这些设备的MTU可能小于发送端的MTU。此时虽然数据包在发送端已经分段过了,但是在IP层就还会再分片一次。如果链路上还有设备有更小的MTU,那么还会再分片,最后所有的分片都会在接收端处进行组装。
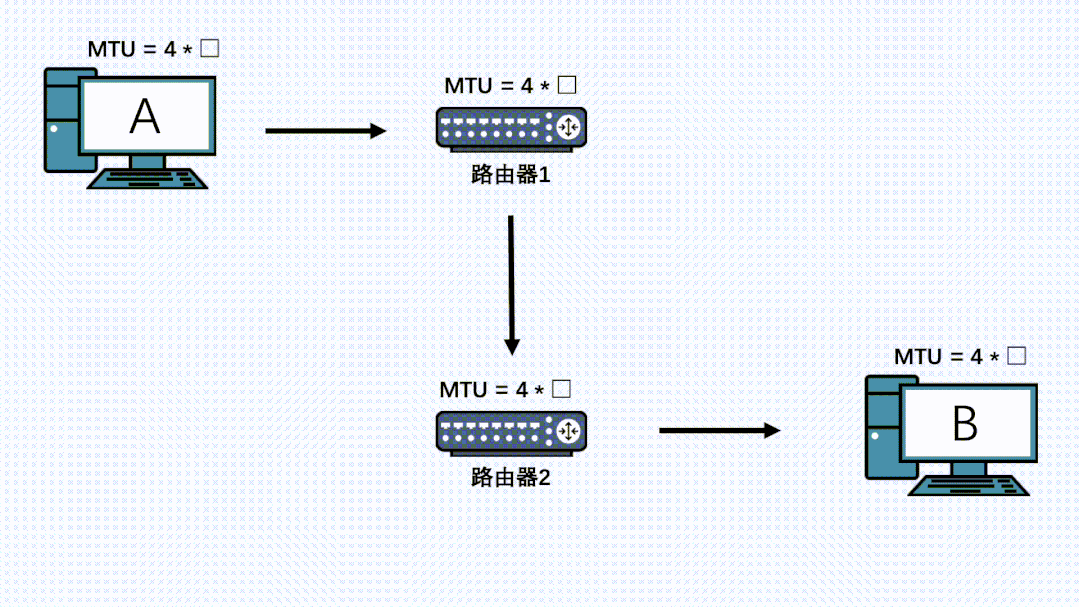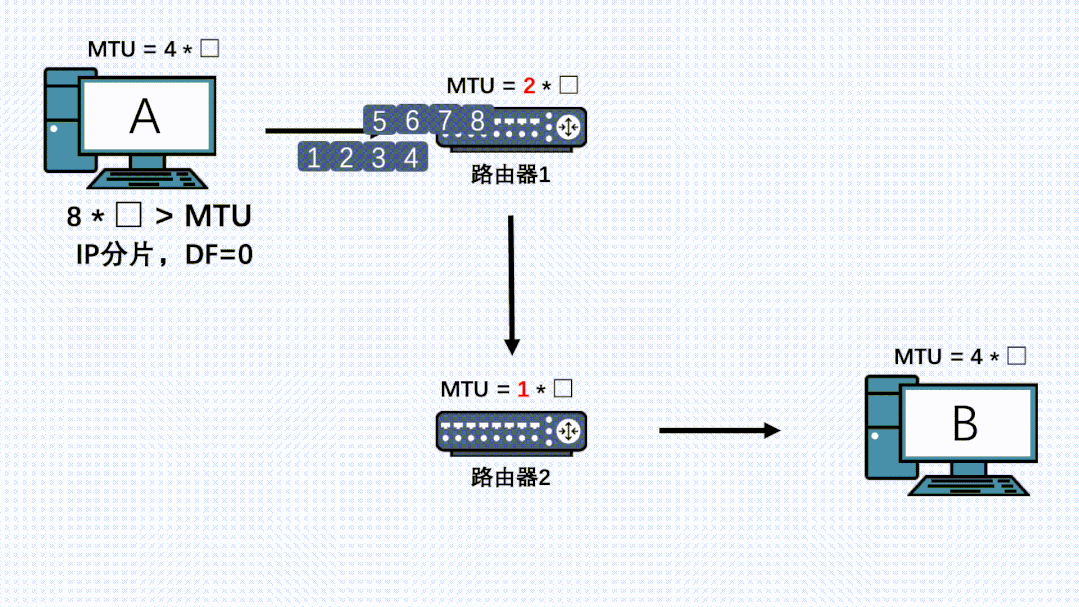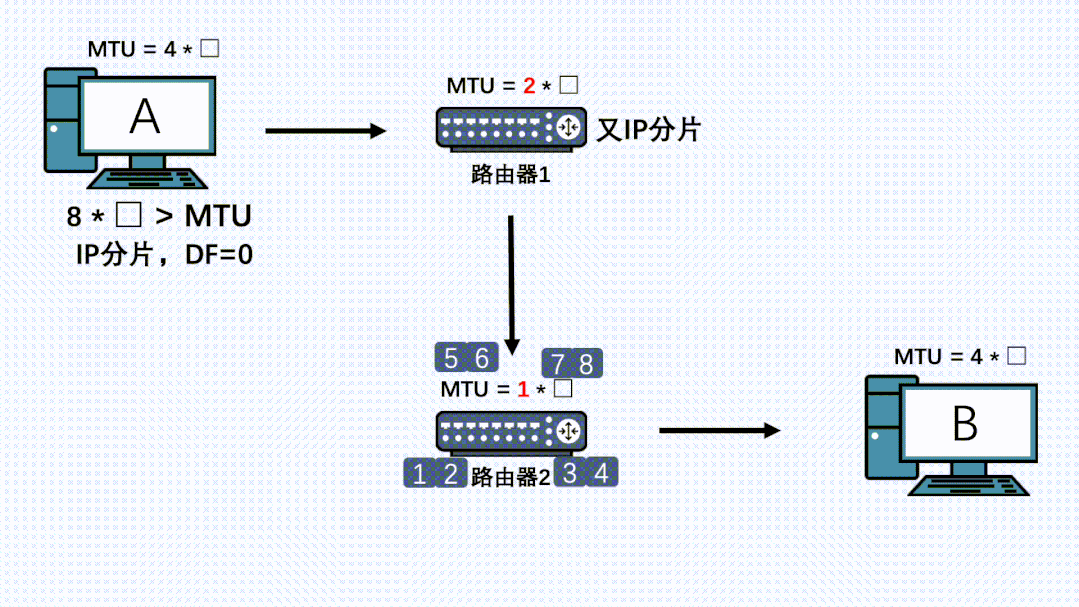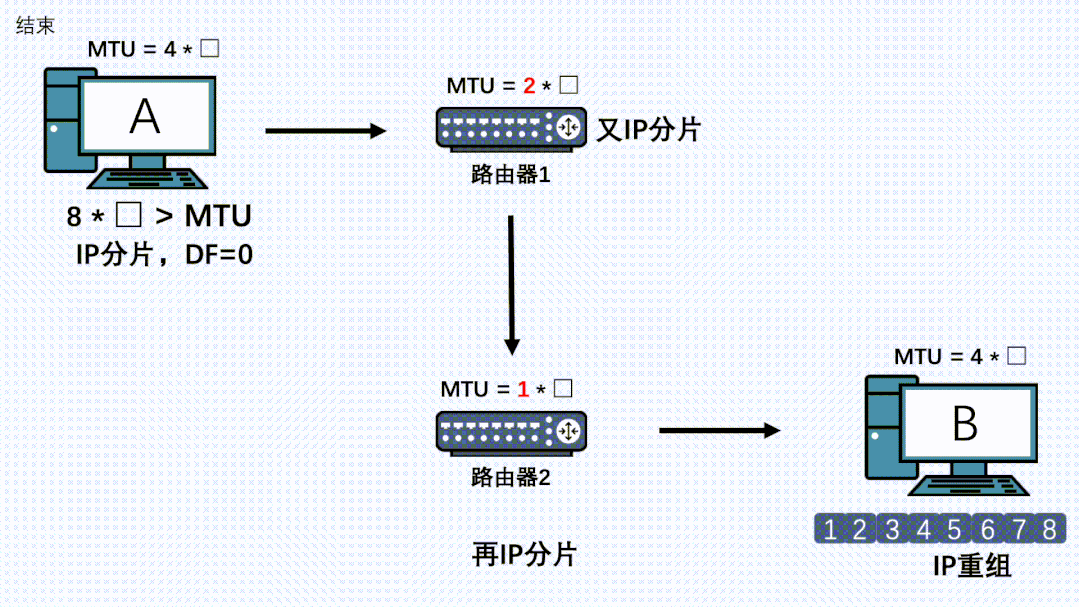
因此,就算TCP分段过后,在链路上的其他节点的IP层也是有可能再分片的,而且哪怕数据被第一次IP分片过了,也是有可能被其他机器的IP层进行二次、三次、四次….分片的。
IP层怎么做到不分片
IP层在传输过程中因为各个节点间MTU可能不同,导致数据是可能被多次分片的。而且每次分片都要加上各种信息便于在接收端进行分片重组。那么IP层是否可以做到不分片?如果有办法知道整个链路上,最小的MTU是多少,并且以最小MTU长度发送数据,那么不管数据传到哪个节点,都不会发生分片。整个链路上,最小的MTU,就叫PMTU(path MTU)。有一个获得这个PMTU的方法,叫 Path MTU Discovery。
原理
原理比较简单,首先我们先看下IP的数据报头。
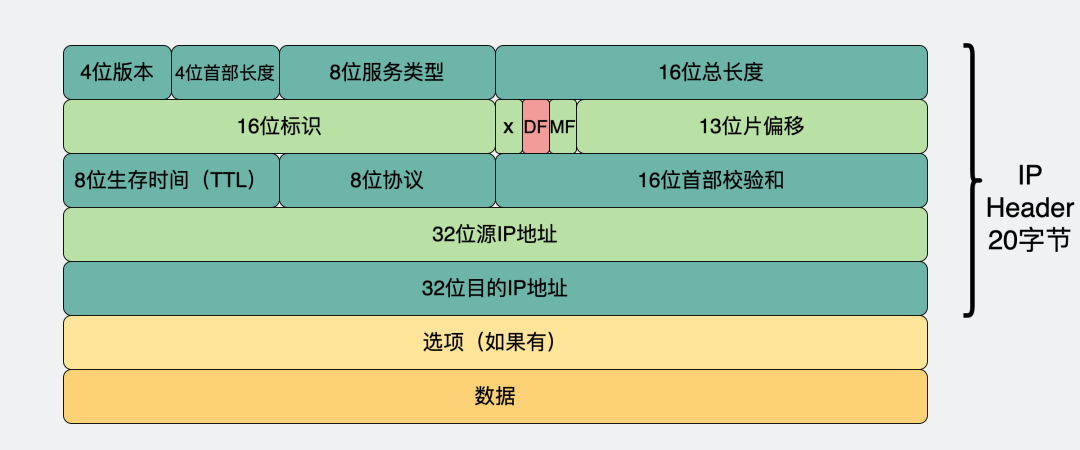
这里有个标红的标志位DF(Don’t Fragment),当它置为1,意味着这个IP报文不分片。
当链路上某个路由器,收到了这个报文,当IP报文长度大于路由器的MTU时,路由器会看下这个IP报文的DF:
- 如果为0(允许分片),就会分片并把分片后的数据传到下一个路由器
- 如果为1,就会把数据丢弃,同时返回一个ICMP包给发送端,并告诉它数据不可达,需要分片,同时带上当前机器的MTU
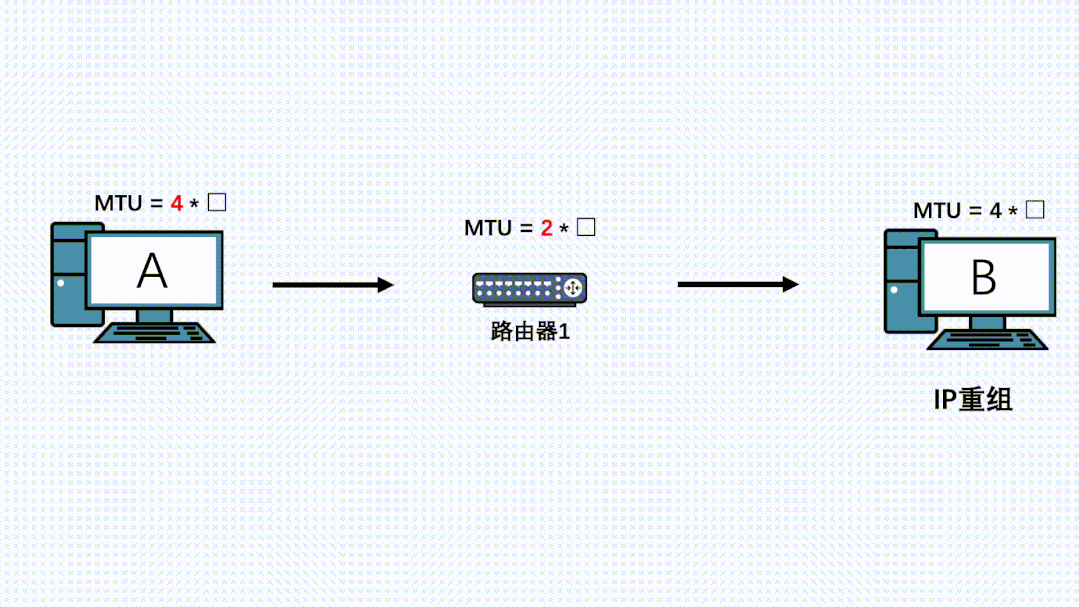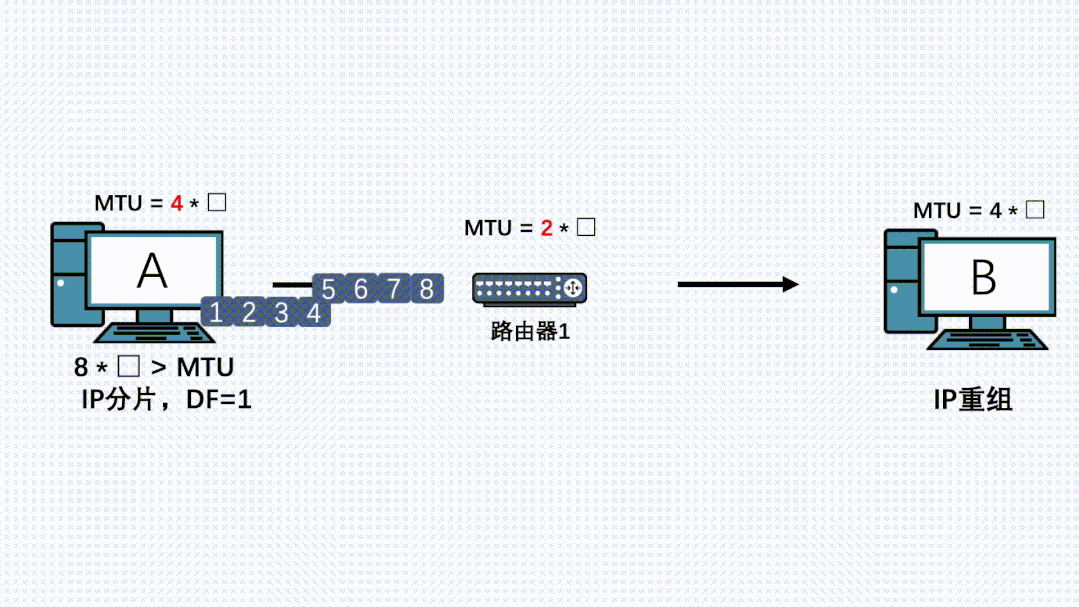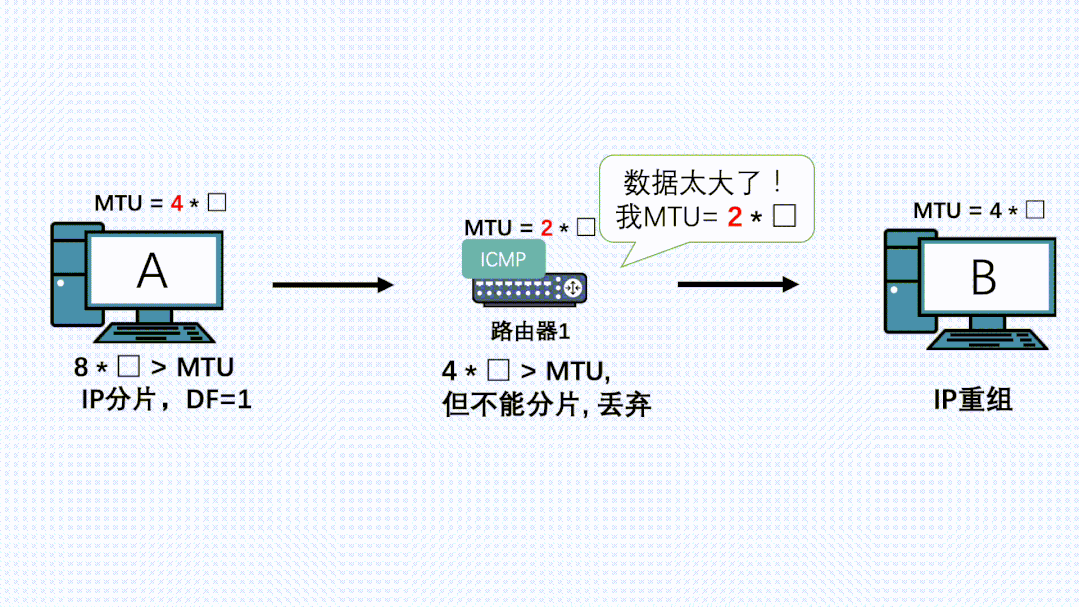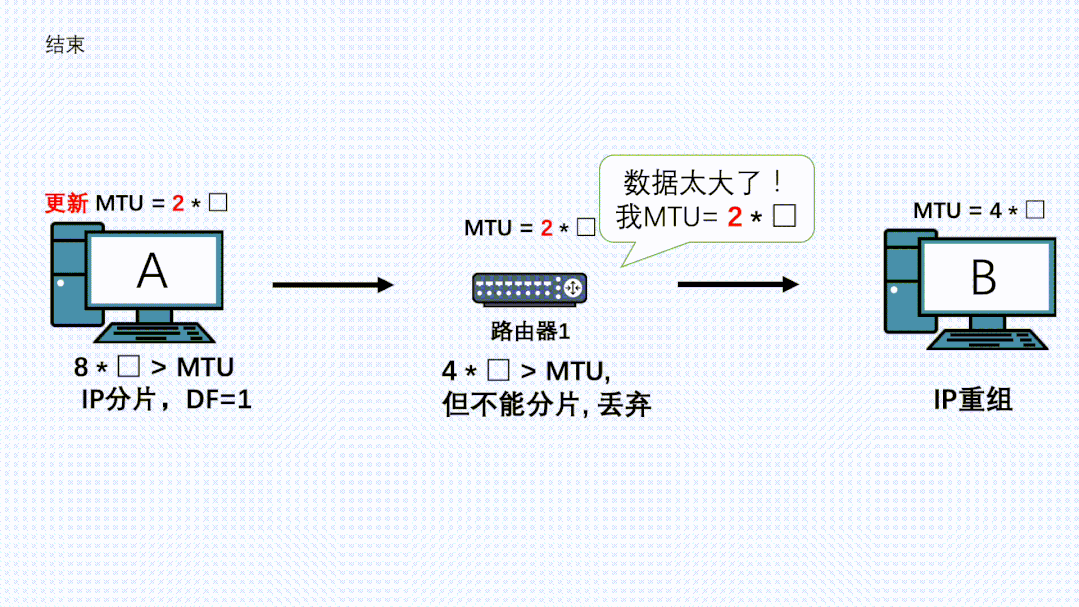
理解了上面的原理后,我们再看下PMTU发现是怎么实现的:
- 应用通过TCP正常发送消息,传输层TCP分段后,到网络层加上IP头,DF置为1,消息再到更底层执行发送
- 此时链路上有台路由器由于各种原因MTU变小了
- IP消息到这台路由器了,路由器发现消息长度大于自己的MTU,且消息自带DF不让分片。就把消息丢弃。同时返回一个ICMP错误给发送端,同时带上自己的MTU
- 发送端收到这个ICMP消息,会更新自己的MTU,同时记录到一个PMTU表中。
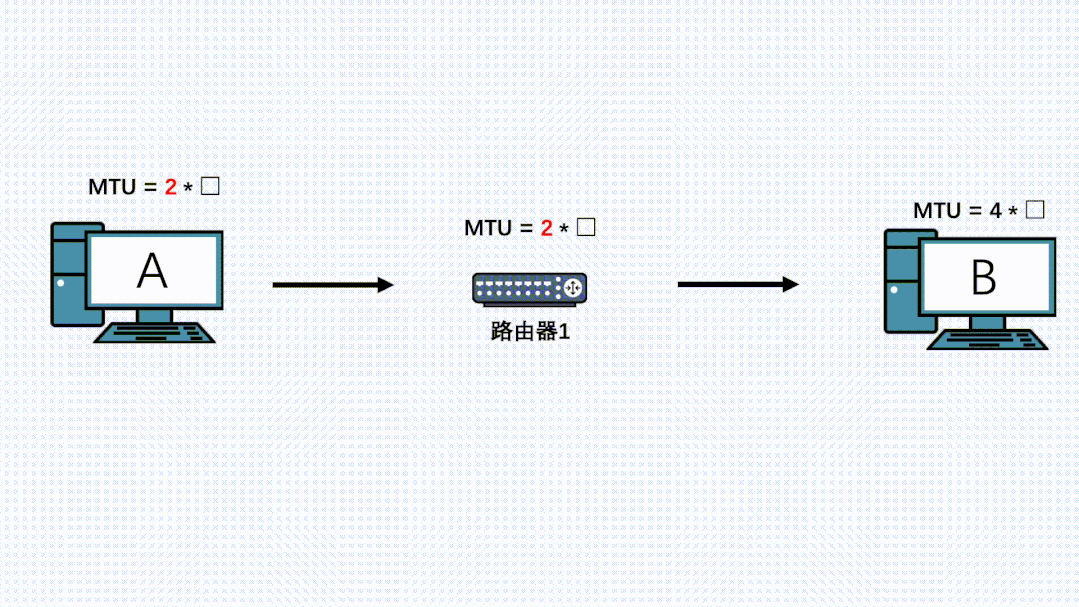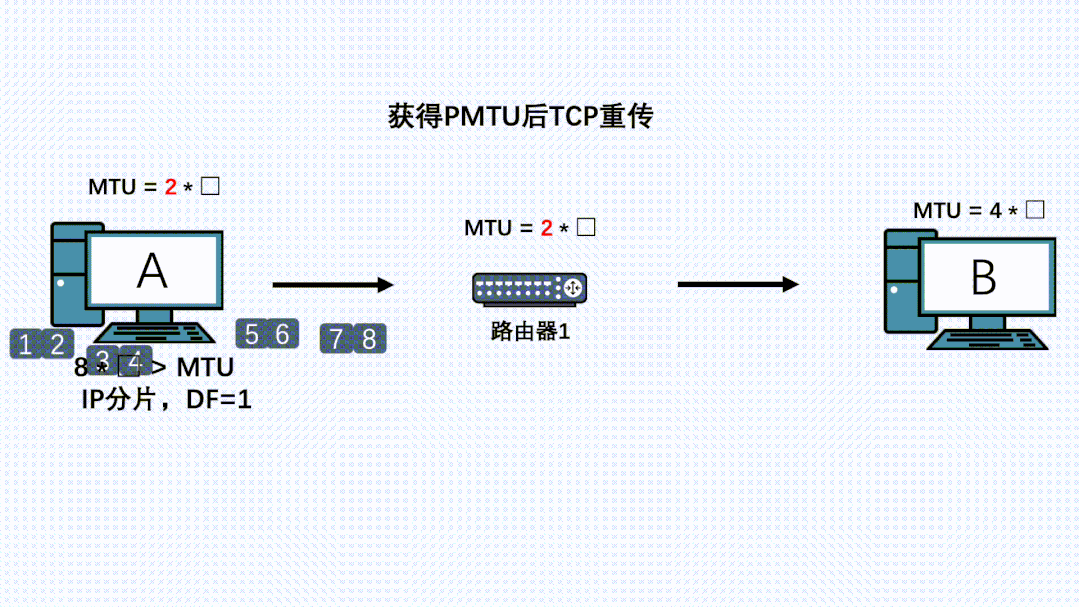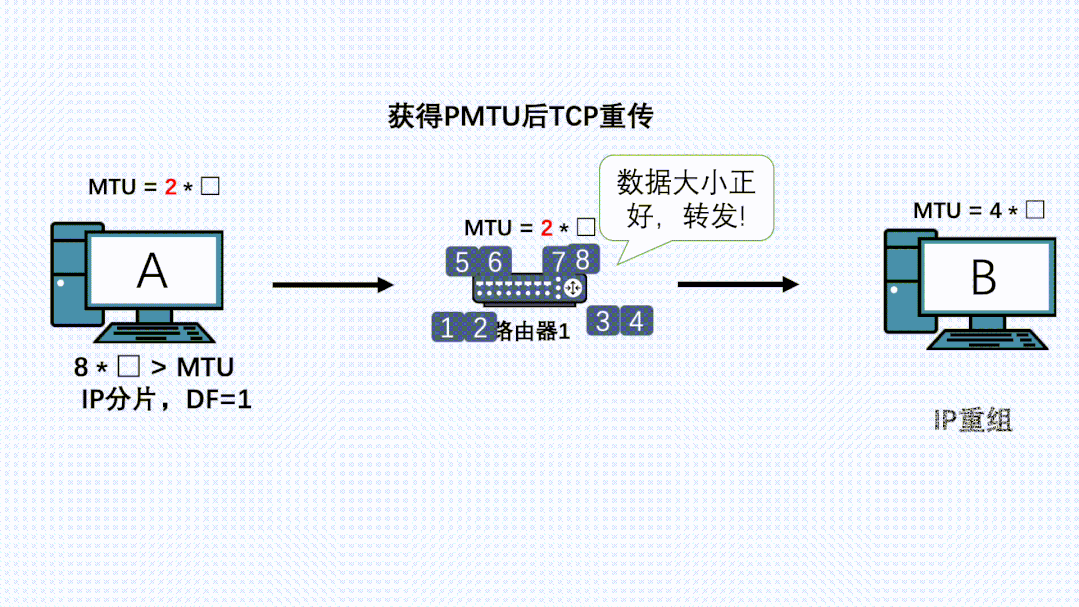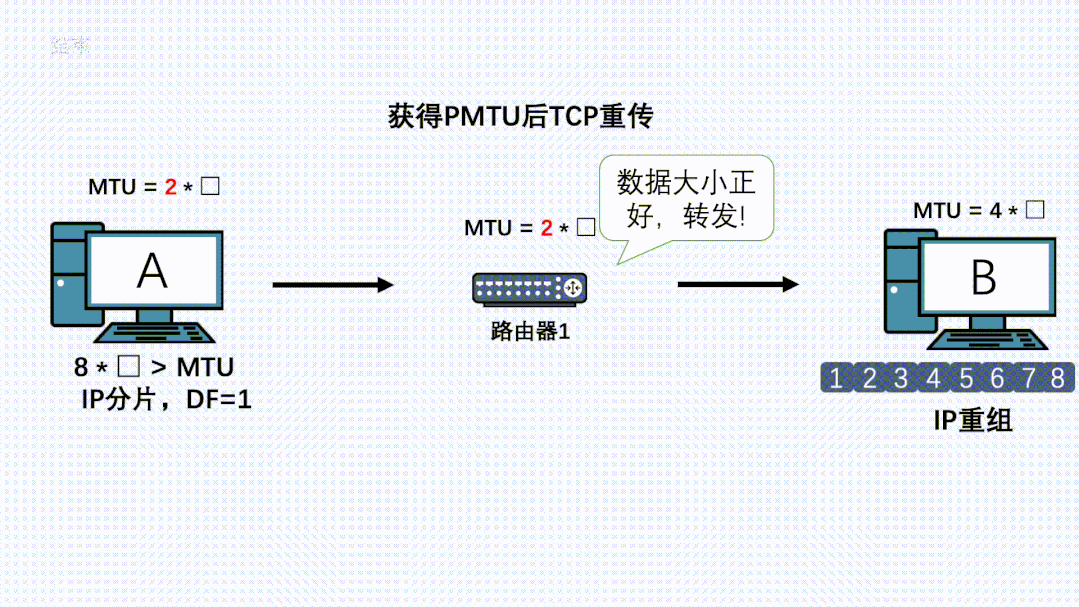
- 因为TCP的可靠性,会尝试重传这个消息,同时以这个新MTU值计算出MSS进行分段,此时新的IP包就可以顺利被刚才的路由器转发。
- 如果路径上还有更小的MTU的路由器,那上面发生的事情还会再发生一次。
Apsara vSwitch(AVS) Jumbo frames support
详情参考SIGCOMM’24 paper: Triton: A Flexible Hardware Offloading Architecture for Accelerating Apsara vSwitch in Alibaba Cloud
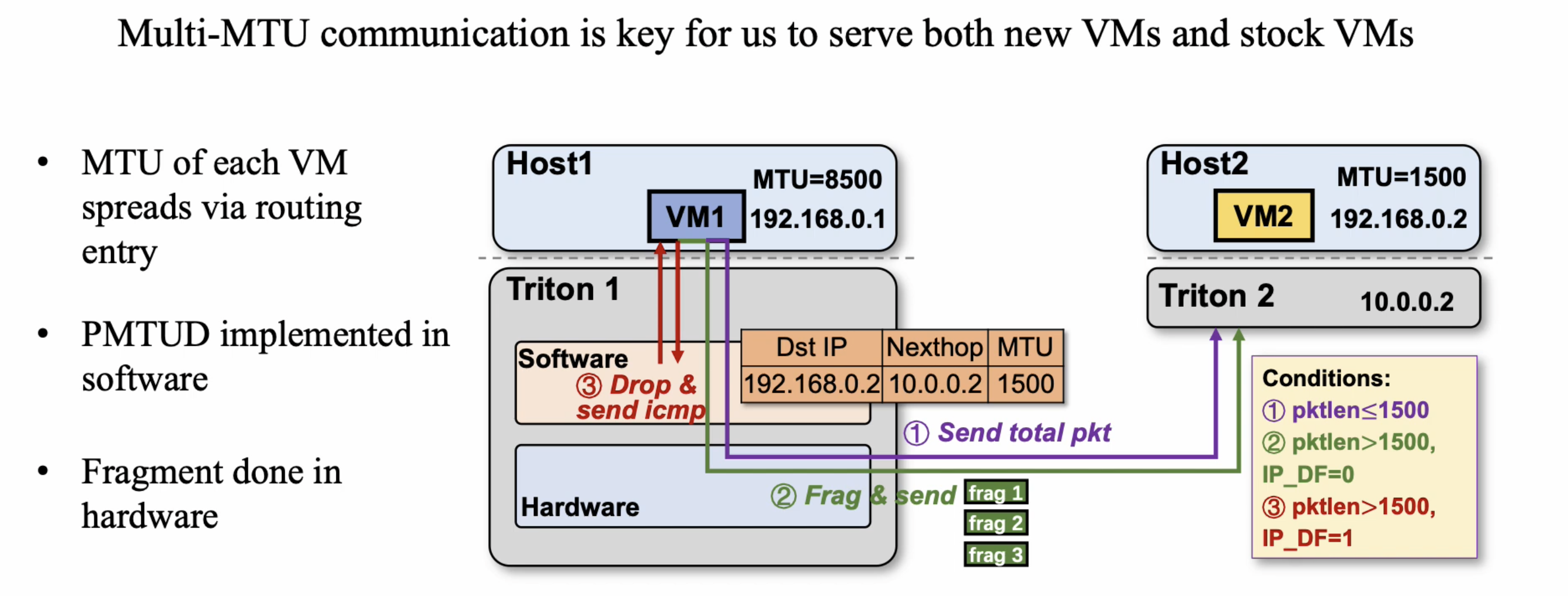
However, supporting jumbo frames in cloud-scale data centers presents more compatibility challenges than supporting it within only a specific cluster. There are a number of stock VMs and out-of-date hardware devices that do not support such a big MTU, but have the demand to communicate with VMs that use 8500 MTU. To make things worse, most hardware switches do not support fragment and Path MTU Discovery(PMTUD) mechanisms. That requires AVS to negotiate MTU and ensure network connectivity for VMs.
To tackle this, we introduces path MTU and new actions to AVS for ensuring network connectivity in multi-MTU scenarios. The controller attaches the path MTU when issuing routing entries to AVS, allowing awareness of the maximum acceptable MTU to the destination. Then AVS employs three new actions as RFC standards, for handling oversized packets. For a packet that is smaller than the path MTU, the AVS will forward the packet as usual. But when the packet is bigger than the path MTU, there will be two different treatments according to the standards. If the Don’t Fragment (DF) field in IP header is set to 1, the packet should be dropped and an ICMP message containing path MTU will be sent to the source VM to reduce packet length. This kind of action is complex and costs too much to generatea new packet in hardware, so we implement it in software AVS. But if the DF field is 0, the packet should be fragmented and sent out. The action is fixed and I/O related, thus is more suitable to be implemented in hardware for efficiency.
参考资料:
- 巨型帧(Jumbo Frames)
- Jumbo Frames and MTU
- Triton: A Flexible Hardware Offloading Architecture forAccelerating Apsara vSwitch in Alibaba Cloud(SIGCOMM’24)
- The Case Against Jumbo Frames
- 动图图解!既然IP层会分片,为什么TCP层也还要分段?
- 路径MTU发现机制(PMTUD)
- Path MTU Discovery PMTUD
- TCP分段与IP分片的区别与联系
- rfc1191