Notes about NVMe FDP feature
本文将mark下NVMe FDP(Flexible data placement)的相关notes。
Key idea
通过host(上层应用)与SSD的协作,将生命周期同步的数据,在写入时就物理地聚集在一起,从而使它们能“同生共死”,极大简化数据清理过程,从根源上解决写放大问题。
从数据写入的源头就开始规划,将同类数据放在一起,从而让整个块的数据能同时失效,极大减少了有效数据搬移,从根本上降低了写放大。
Architecture
The Flexible Data Placement interface provides abstractions to the host to group data on the device with a similar expected lifetime(e.g., death time). The interface introduces the following concepts to expose the SSD physical architecture.
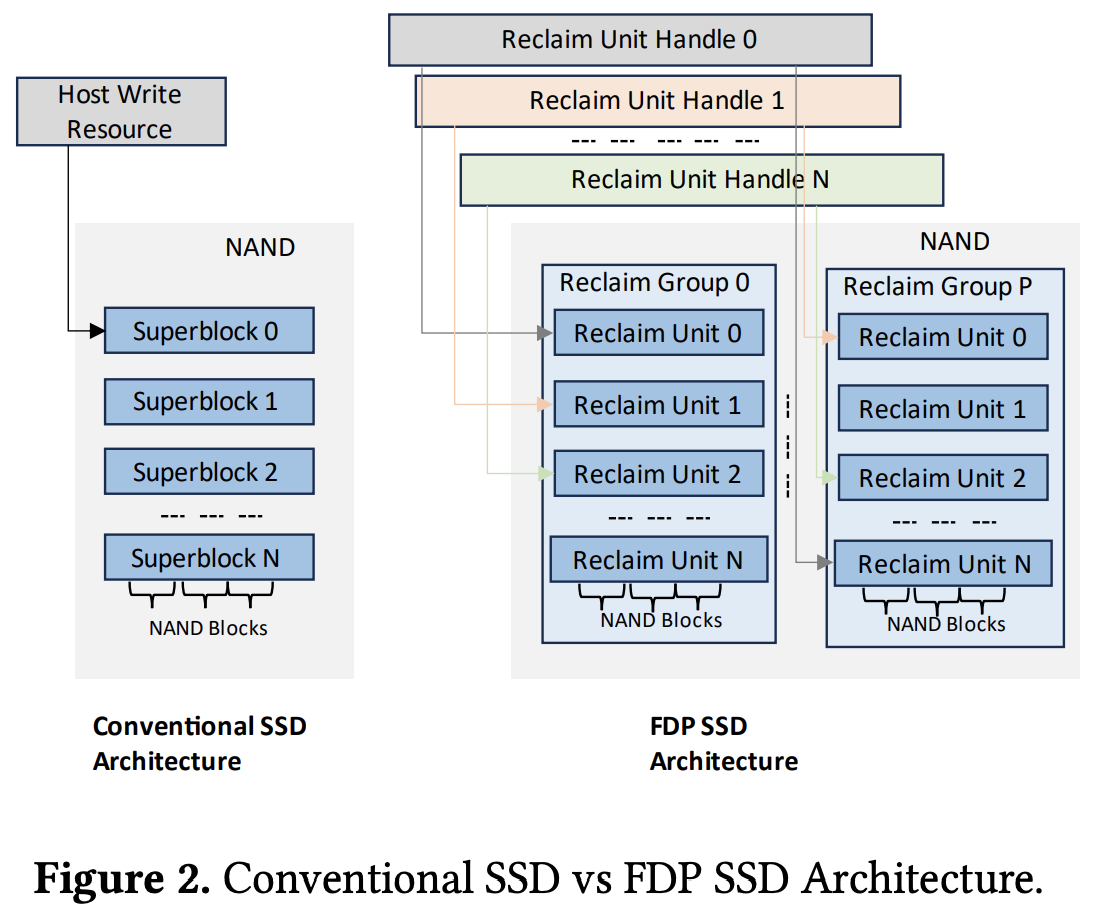
Reclaim Unit (RU)
The NAND media is organized into a set of reclaim units where a reclaim unit consists of a set of blocks that can be written. A reclaim unit will typically consist of one or more erase blocks.
Reclaim Group (RG)
A reclaim group is a set of reclaim units.
Reclaim Unit Handles (RUH)
A reclaim unit handle is an abstraction in the device controller similar to a pointer that allows host software to point to the reclaim units in the device. Since a reclaim unit is not directly addressable by the host, the host software uses the reclaim unit handles to logically isolate data. The device manages the mapping of reclaim unit handles to a reclaim unit and has complete control over this mapping. The number of RUHs in the device determines the number of different logical locations in the NAND where the host software can concurrently place data.
总结
通过数据隔离,当一个应用的数据失效时,其对应的整个RU可以直接被擦除回收,大幅减少了垃圾回收所需搬移的数据量。理想情况下,可以将写放大系数降低至接近1。
参考资料: