Introduction to Intel I/OAT
本文将介绍Intel I/OAT(I/O Acceleration Technology)相关知识点。
1. Overview
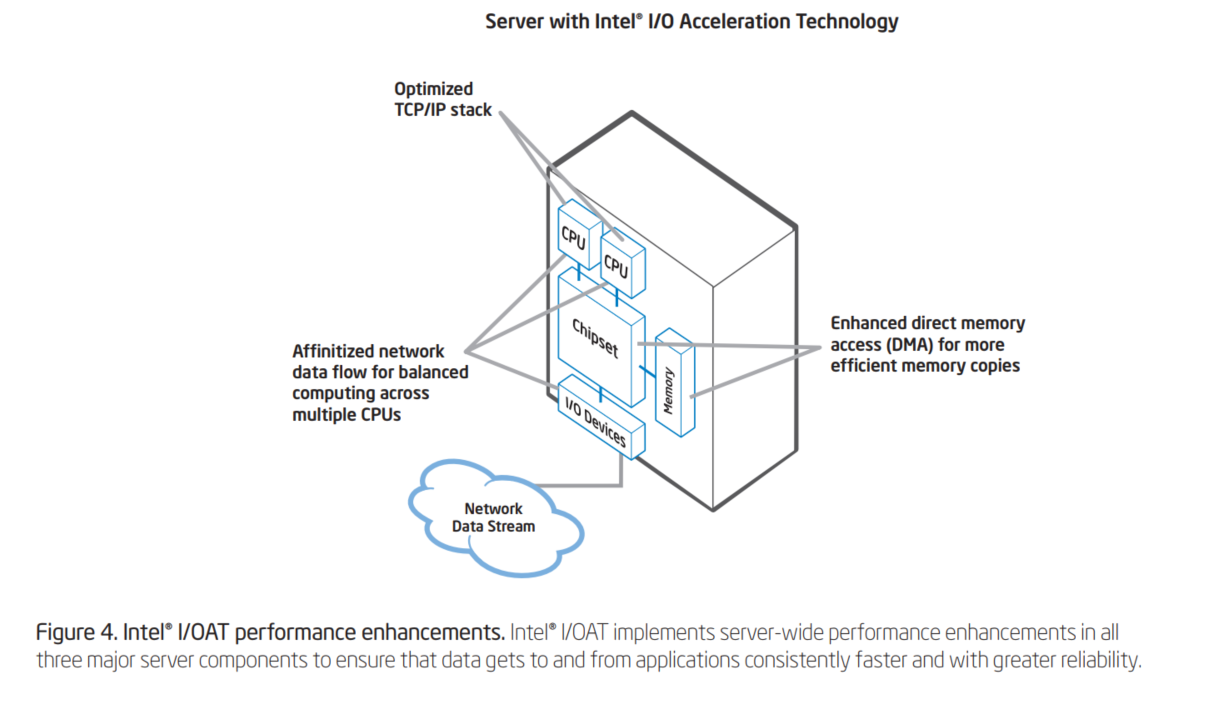
Intel I/OAT is actually a set of technologies that each contributes to increased performance.
The features of Intel I/OAT enhance data acceleration across the computing platform.
- Intel® QuickData Technology enables data copy by the chipset instead of the CPU, to move data more efficiently through the server and provide fast, scalable, and reliable throughput.
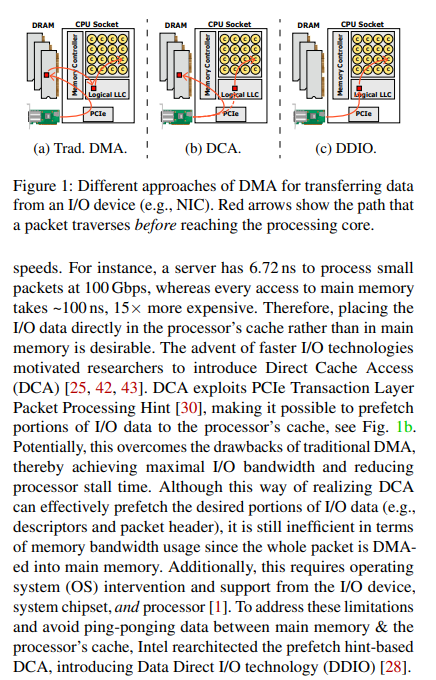
- Direct Cache Access (DCA) allows a capable I/O device, such as a network controller, to place data directly into CPU cache, reducing cache misses and improving application response times.
- Extended Message Signaled Interrupts (MSI-X) distributes I/O interrupts to multiple CPUs and cores, for higher efficiency, better CPU utilization, and higher application performance.
- Receive Side Coalescing (RSC) aggregates packets from the same TCP/IP flow into one larger packet, reducing per-packet processing costs for faster TCP/IP processing.
- Low latency interrupts tune interrupt interval times depending on the latency sensitivity of the data, using criteria such as port number or packet size, for higher processing efficiency.
本文只介绍QuickData Technology和DCA。
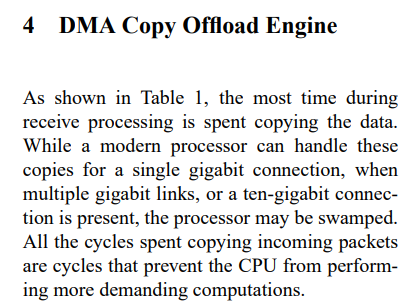
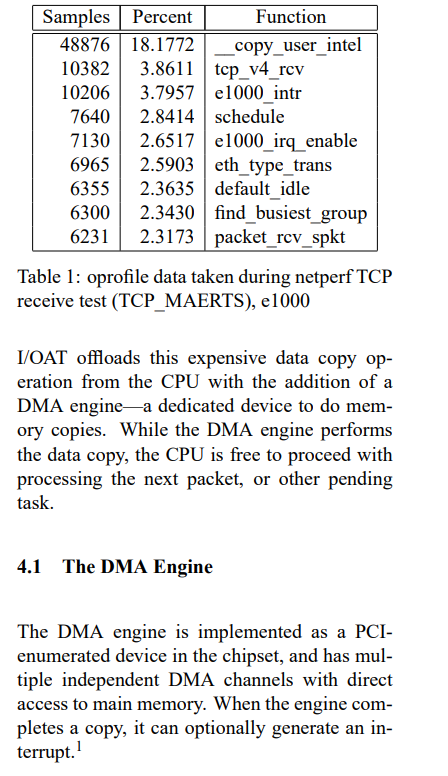
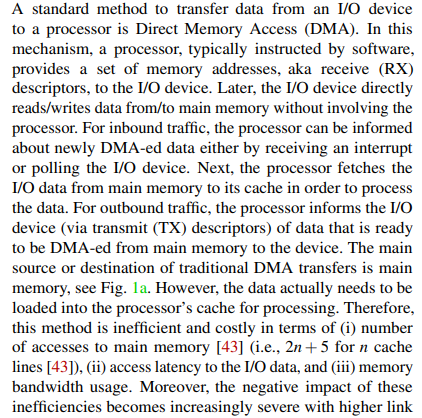
2. Intel® QuickData Technology
Intel® DSA replaces the Intel® QuickData Technology.
3. Direct Cache Access (DCA)
Introduction to Intel DDIO technology
参考资料:
- White Paper
- Intel® I/O Acceleration Technology
- Reexamining Direct Cache Access to Optimize I/O Intensive Applications for Multi hundred-gigabit Networks
- Using Intel IOAT DMA
- Tanveer_Alam_Enterprise_Storage_RAS_Augmented_native_Intel_Platform_Storage_Extensions.pdf
- Accelerating Network Receive Processing
- 关于intel的IOAT技术
- Efficient Asynchronous Memory Copy Operations on Multi-Core Systems and I/OAT